Precision fermentation’s promise to revolutionise food
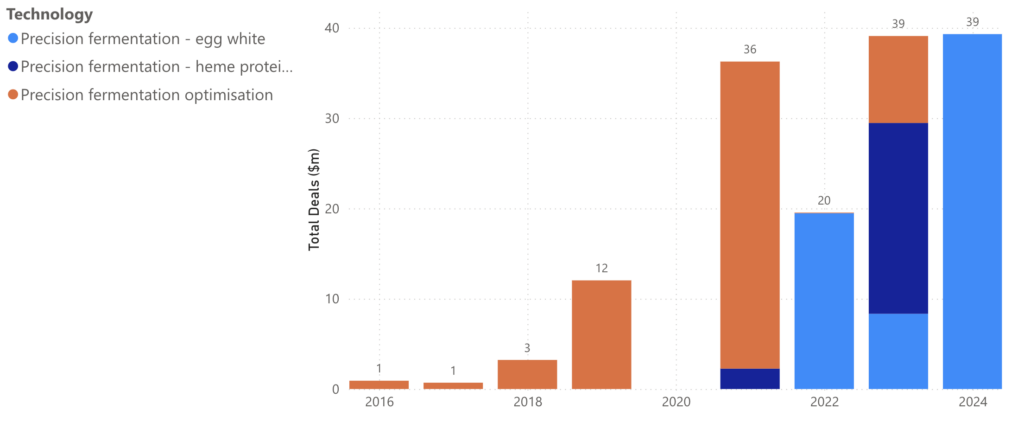
Figure 1. Annual fund-raising deals: fastest-growing precision fermentation themes
By Jenna Chow
Food production processes today rely heavily on agriculture and animal husbandry, bringing huge, negative environmental risks. As such, the food industry is actively seeking sustainable and animal-free alternatives to traditional ingredients. One of the fast-growing technologies in this field is precision fermentation.
Precision fermentation is a bio-engineering process that involves programming microorganisms with specific genetic codes, to produce ingredients that are molecularly identical to traditional food components.
This technology has the potential to disrupt the existing food industry, by providing more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective methods of producing animal-free dairy, egg proteins and fats.
During precision fermentation, genetically modified (GM) microorganisms are used as a factory to produce the target food ingredients. Thus, the end products themselves do not contain any genetically modified components.
However, the classification of these products varies among countries.
In the US and UK, they are not considered GM foods, whereas in China, they are classified as such. The European Union is still debating its classification.
Besides regulatory and classification challenges, scaling and cost are important hurdles that the precision fermentation market is actively addressing. To gain widespread acceptance and adoption, it is crucial their costs are comparable to those of traditional food production, which relies on low-cost ingredients.
According to The Food Institute, achieving ingredient costs below US$25/kg for precision fermentation-based products will continue to be a challenge in the next few years.
Despite hurdles in this bumpy market, funding in the fermentation sector was steady at around $900 million last year, and is on track to surpass that in 2024, New Food Finance data show. We also observe increased investment by multinational food companies, such as Nestlé, Mars, and Cargill.
At New Food Finance, we analyse how technologies and companies are fostering a positive environmental transition in the food production chain, at a granular level.
Despite observing some slowdown in certain precision fermentation sub-sectors, such as milk proteins, our database reveals three growing sectors to look out for:
Animal-Free Egg White
Animal-Free Egg White can reduce the environmental and animal welfare burdens associated with traditional egg production. In addition, the recent bird flu outbreak has heightened interest in precision fermentation alternatives.
Onego Bio is at the forefront, developing animal-free egg white, ovalbumin, by introducing a genetic blueprint into a selected microbe. The resulting product is an egg-white powder that can be used in various applications, including baking. The company has raised over $67mln to date, including a recent $30mln round in 2024, marking one of the largest investments in precision fermentation.
Animal-Free Heme
Companies have been exploring ways to improve the aroma, taste, appearance, and nutrient content in plant-based meats. One method is using animal-free heme proteins, that are biologically identical to animal proteins. Heme is an essential molecule abundantly found in the blood of animals. It is what gives meat its meaty taste. Heme can also be found in plants, but in much lower concentrations.
In addition to notable companies like Impossible Foods, which produces soy-derived heme, emerging companies like Paleo are gaining attention. Paleo uses genetically modified yeast to produce heme proteins, aiming to improve the taste and healthiness of plant-based foods. The company completed a €12mln Series A funding round early last year.
Precision Fermentation Optimization
Besides developing individual food ingredients, efforts are underway to enhance precision fermentation processes, aiming to reduce costs and time, thus making products more scalable and affordable.
Pow.Bio has developed a technology to increase the efficiency of precision fermentation, by enabling continuous fermentation, which reduces capital expenditure and boosts manufacturing capacity. Recently, the company announced a partnership with MeliBio to scale up the production of bee-free honey via improved precision fermentation.
In a nutshell, watch this space. As precision fermentation technology continues to advance, we expect more companies to enter this space, and more innovative products to hit the market.
